What Is Big Data? What Are The Three Big Data Types?

Big data refers to the enormous, difficult-to-manage volumes of structured and unstructured data that daily deluge enterprises. However, more important than just the type or quantity of data is what organizations do with it. When making crucial business decisions, big data analysis can generate insights that aid in decision-making and offer certainty. Big Data is a sizable body of data that is continually expanding exponentially. Due to its size and complexity, no traditional data management system can store or process this data adequately.
The importance of big data depends on more than just how much data you have. Your use will determine its value. You can find solutions that simplify resource management, boost operational effectiveness, enhance product development, spur new income and growth prospects, and facilitate wise decision-making by getting data from any source and analyzing it. Big data and high-performance analytics can be used to complete a variety of business-related tasks.

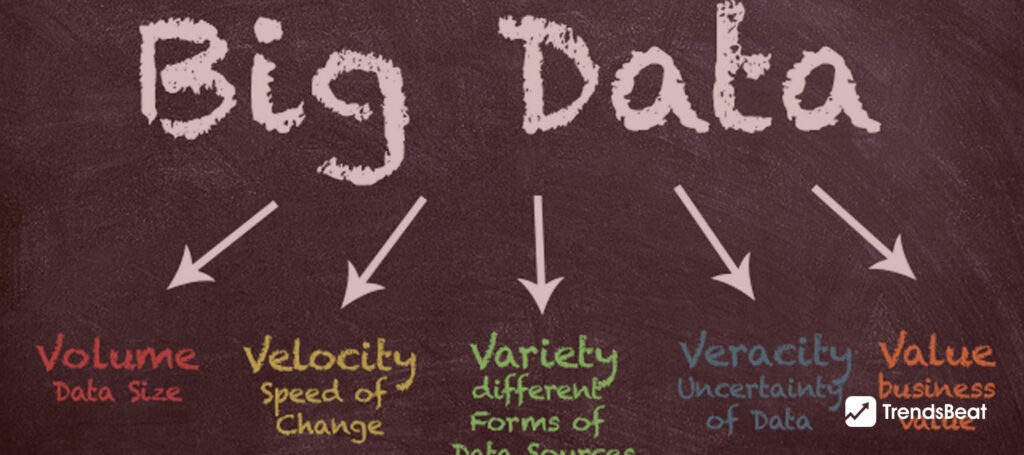
Big data is just a more extensive, complex collection of data that has been gathered from various, both new and old sources. Because the data sets are so large, conventional data processing software is unable to handle them. These enormous amounts of data are typically employed to solve business challenges that you might not be able to handle. Volume, variety, velocity, value, and veracity are the five vs. that can be used to describe the characteristics of big data. These traits not only help us understand big data, but they also give us a sense of how to handle massive, fragmented data at a manageable speed in an appropriate amount of time so that we may get value from it, perform real-time analysis, and act quickly.
What Are The Three Big Data Types?
Incredibly large amounts of data are produced every second as the Internet age progresses. In fact, it is predicted that by 2025, there will be 163 zettabytes of data on the internet. Tweets, snaps, purchases, emails, blog posts, and anything else we can think of are included in that amount of digital data. This information can be categorized into the following types:
Structured Data
Simply said, structured data is information that is stored in a specified field within a record. It is the kind of data that is most prevalent in our daily lives. like your birthday or address. It is bound by a specific schema, giving all the data the same set of attributes. Relational data is another name for structured data. By constructing a single record to represent an entity, it is divided across several tables to improve the integrity of the data. Application of table constraints enforces relationships. Structured data has an economic value based on how well a company can use its current systems and procedures for analysis.
It is simple to enter, search, and analyze structured data. The format of the data is the same for all of it. However, imposing a uniform structure also makes it difficult to change data because each record must be modified to follow the new structure. Numbers, dates, strings, and other types of data are examples of structured data. An e-commerce website’s business data can be regarded as structured data. In a data warehouse, structured data is kept under strict restrictions and according to a predetermined schema. All of that structured data would need to be updated in response to any change in requirements. In terms of managing resources and time, this has a significant disadvantage. Only in situations where established functionalities are present, structured data can be used. Structured data, as a result, has little flexibility and is only appropriate for a restricted number of use cases.
Unstructured Data
Unstructured data is any type of data that doesn’t follow a specific schema or set of guidelines. Its layout is chaotic and ill-thought-out. Unstructured data is often referred to as images, videos, text documents, and log files. Although a picture or video may have semi-structured metadata, the underlying data being processed is unstructured.
Unstructured data is additionally referred to as “black data” since it cannot be examined without the right computing tools. Unstructured data is any data that is not predetermined in terms of shape or order. Unstructured data is enormous in quantity and presents a number of processing obstacles that must be overcome in order to extract value from it.

Unstructured text files, along with photos, videos, and other sorts of data, are frequently found in heterogeneous data sources, which also contain other types of data. Organizations nowadays have access to a lot of data, but they are unable to add value to it because it is unstructured or raw.
Semi-Structured Data
Semi-structured data is not restricted by a fixed schema for managing and storing data. The data is not neatly arranged into rows and columns like that in a spreadsheet, nor is it in a relational structure. However, other characteristics, like key-value pairs, aid in differentiating the various entities from one another.
Semi-structured data is sometimes known as NoSQL data because it doesn’t require a structured query language. Semi-structured data is exchanged between systems, some of which may even have different underlying infrastructures, using a data serialization language. Semi-structured material can also contain files holding the code for computer programs, however, it is frequently used to store metadata about business processes. Typically, external sources for this kind of information include social media platforms. Both the above-mentioned types of data can be found in semi-structured data. Semi-structured data can appear to be structured, but it is not defined by the concept of a table, for instance, in a relational DBMS. Semi-structured data is exemplified by an XML file containing data.
Summary
In conclusion, there are three types of application data: structured, semi-structured, and unstructured. Structured data follows a predetermined set of principles and is properly ordered. Although semi-structured data doesn’t follow any specific schema, it has several distinguishable characteristics for an organization. Data objects are transformed into byte streams using data serialization languages. These consist of YAML, JSON, and XML. There is absolutely no organization in unstructured data. An application contains data from each of these three categories. They all have equally crucial roles to play in creating inventive and appealing applications.








































































![Essential-Cybersecurity-Tips-for-Small-Businesses-[Protect-Your-Data]-TrendsBeat](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Essential-Cybersecurity-Tips-for-Small-Businesses-Protect-Your-Data-feature-image-template-1024x455.jpg)
















![Top Fitness Trends & Workout Routines to Follow [Stay Fit, Stay Healthy]](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/feature-image-Top-Fitness-Trends-Workout-Routines-to-Follow-Stay-Fit-Stay-Healthy-1024x455.jpg)









![[Weight Loss Medication Health Effects] Side Effects and Best Advice](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/feature-image-Weight-Loss-Medication-Health-Effects-Side-Effects-and-Best-Advice-1024x455.jpg)



