How Does A Plant-Based Diet Affect Overall Health?
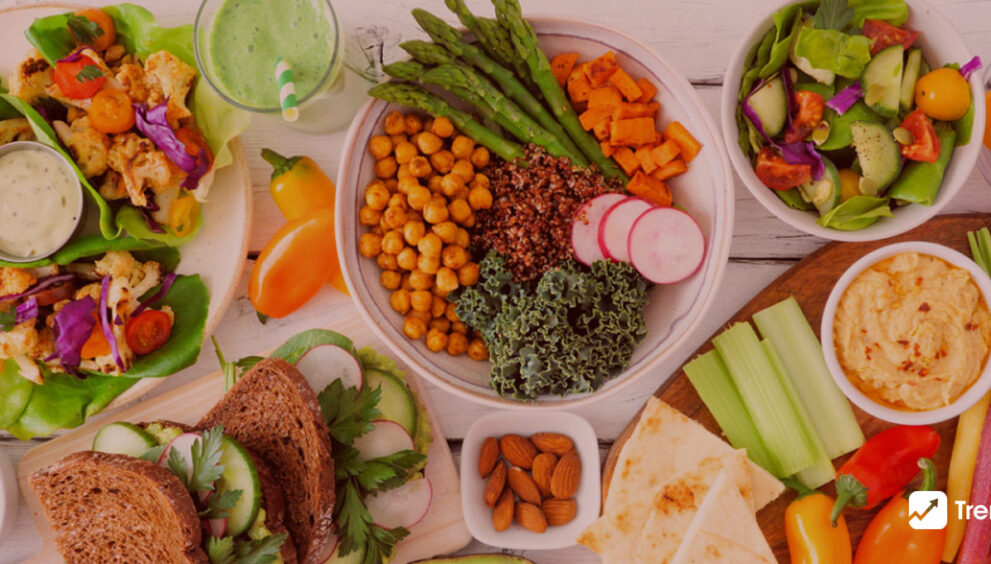
How do plant-based diet and health are related? A plant-based diet consists solely of plant foods such as fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes and excludes meat, dairy, and eggs. Plant-based meals are high in fibre, high in vitamins and minerals, and low in calories and saturated fat. Consuming a range of these meals supplies your body with all of the protein, calcium, and other critical nutrients it requires. It is critical to incorporate a dependable supply of vitamin B12 into your diet. A daily supplement or fortified foods, such as vitamin B12-enriched morning cereals, plant milk, and nutritional yeast, can easily satisfy your vitamin B12 needs. Plant-based diets reduce the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and other health problems. In this blog, we have discussed the nutritional benefits of a plant-based diet, how a plant-based diet help in chronic disease prevention, and how it can impact cardiovascular health.
What Are The Nutritional Advantages Of Eating A Plant-Based Diet?
Improved Cardiovascular Health
“Plant-based diets typically have reduced saturated fat consumption and greater unsaturated fat and fibre intake, which is connected to a lowered risk of cardiovascular disease, obesity, and type 2 diabetes.
Plant-Based Diet Keeps Your Mind Sharp
Indeed! Plant-based diet and health are associated. There are several physiological benefits to eating a plant-based diet, but there may also be some mental ones. Researchers at Boston University School of Medicine discovered that consuming more plant-based meals like berries and green leafy vegetables while restricting your intake of foods high in saturated fat and animal products might slow down heart failure and lessen your risk of cognitive decline and dementia.
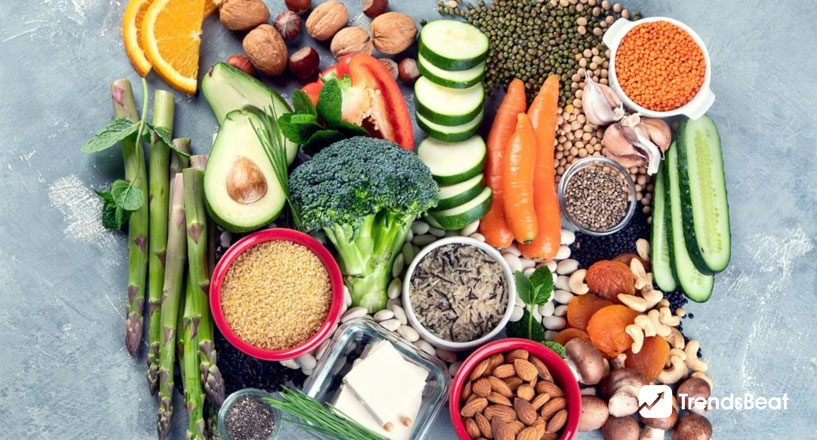

Better Gut Health
Vegetarian and vegan diets have been demonstrated to support a healthy balance of beneficial bacteria, hence improving gut and general health. A plant-based diet can make it much simpler to get the necessary 30g of dietary fiber each day, which will benefit your gut health. Many bacteria in your gut feed on fibre and specific prebiotics and generate beneficial short-chain fatty acids that promote human health, including hunger management.
A study published in Frontiers in Nutrition discovered that a plant-based diet results in a more diversified and stable microbiome. A plant-based diet should ideally include a variety of plants every day, as this can boost our microbial health and hence our gut health.
Increased Energy Level
Feeling sluggish after a heavy meal? Plant-based diets can help you avoid post-meal drowsiness and boost your energy levels throughout the day. A primarily plant-based whole-food diet provides your body with the bioavailable nourishment it requires to flourish. Your body can properly break down complete meals and absorb & utilize the nutrients they supply. Hence, one of the amazing nutritional benefits of a plant-based diet is the increased energy level.
How Does A Plant-Based Diet Prevent Chronic Diseases?
Numerous pieces of research emphasized the health benefits of a vegetarian or plant-based diet for chronic disease prevention. The findings imply that eating healthy diets lowers the risk of chronic illnesses, including heart disease and diabetes, weight increase, and mortality, and has several nutritional benefits. The researchers also stated that consuming high-quality plant-based foods is critical to reaping all the advantages. Vegans are less likely to suffer chronic diseases than other dietary groups, according to a study financed by the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute.
Researchers examined the diets of vegans, lacto-ovo-vegetarians, semi-vegetarians, pesco-vegetarians, and non-vegetarians, as well as many health indicators. In comparison to the other groups, the vegan group had the lowest risk for cancer, heart disease, and hypertension based on those indicators. The vegan group also had greater blood levels of carotenoids and isoflavones, which are associated with decreased inflammation. Vegans ingested the most fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, the most beta-carotene and fibre, and the least saturated fatty acids. The vegan group was the only one that was in a healthy weight range, whereas all other groups were, on average, overweight. These findings provide further light on the link between diet-related biomarkers and illness and also lend credence to a plant-based diet as a healthy strategy to disease prevention.
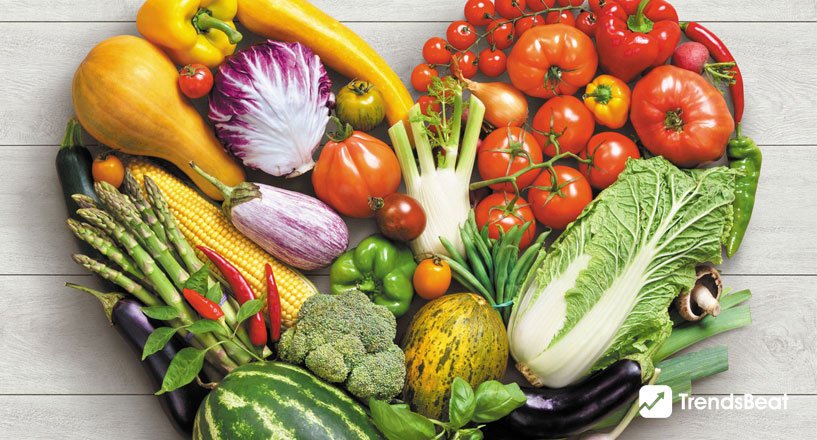

Chronic Diseases Prevention with Plant-Based Diet!
Undoubtedly, a plant-based diet and health are linked. Decades of scientific studies have shown that eating a plant-based diet and avoiding animal-derived foods is the greatest approach to preventing chronic illness and living a healthier, longer life. Overweight and obesity, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and cancer are all lowest among vegans and vegetarians. A healthy vegan diet, often known as a whole food plant-based diet, is one of the healthiest eating options. Because it is strong in antioxidants and phytonutrients, which work to fight inflammation, the major driver of chronic illness, this diet can treat the fundamental cause of chronic disease.
How Does A Plant-Based Diet Impact Cardiovascular Health?
Plant-based diets, defined as consuming animal foods seldom, are increasingly being advised for their health advantages. Many studies have demonstrated that plant-based diets, particularly those high in quality plant foods, including whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and nuts, are related to a decreased risk of cardiovascular events and intermediate risk factors. The current evidence base examining the associations of plant-based diets with cardiovascular endpoints is summarized in this review, as are the potential biological mechanisms underlying their health effects, practical recommendations and applications of this research, and future research directions. Plant-based diets should be promoted as an ecologically friendly dietary alternative for better cardiovascular health.
According to the research, reducing your intake of animal products and eating primarily plant-based diets can lower your risk of heart disease by minimizing the negative effects of a gut-microbiome associated with an increased risk of coronary heart disease. The gut microbiota of the body is made up of a variety of bacteria that play significant roles in metabolism, nutritional absorption, energy levels, and immune response. As gut bacteria consume nutrients contained in animal products such as red meat, a metabolite known as trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) is generated. It has been linked to an elevated risk of heart attack and coronary heart disease (CHD). A vegan or vegetarian diet has been shown to lessen the risk of cardiovascular health.
Few Final Thoughts
This blog is aimed to provide information on plant-based diets and health and the nutritional benefits of being on a vegan-based diet. There are numerous nutritional benefits of a plant-based diet, including improved cardiovascular health, mental sharpness, better gut health, and increased energy levels. We have also discussed chronic disease prevention and how can a plant-based diet impact cardiovascular health.








































































![Essential-Cybersecurity-Tips-for-Small-Businesses-[Protect-Your-Data]-TrendsBeat](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Essential-Cybersecurity-Tips-for-Small-Businesses-Protect-Your-Data-feature-image-template-1024x455.jpg)
















![Top Fitness Trends & Workout Routines to Follow [Stay Fit, Stay Healthy]](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/feature-image-Top-Fitness-Trends-Workout-Routines-to-Follow-Stay-Fit-Stay-Healthy-1024x455.jpg)









![[Weight Loss Medication Health Effects] Side Effects and Best Advice](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/feature-image-Weight-Loss-Medication-Health-Effects-Side-Effects-and-Best-Advice-1024x455.jpg)



