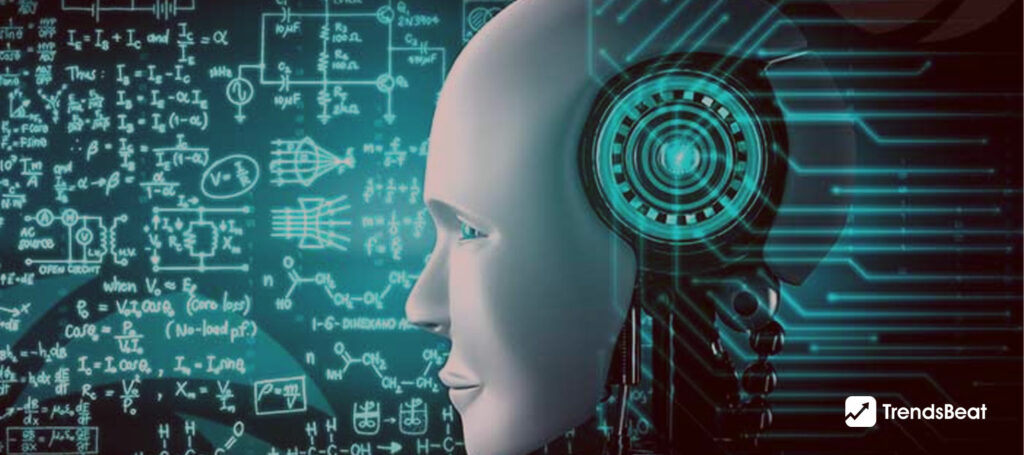
What Is Cognitive AI? Cognitive Computing Vs. Artificial Intelligence?

Nothing beats human reasoning in any manner. Most programmers are on the verge of developing a computer system that can think and reason without human interaction. Essentially, they are developing cognitive artificial intelligence, which can convert human cognition into a computational model. Basically, a cognitive computer is a system that learns at scale, reasons with purpose, and interacts naturally with humans. Instead of being programmed, these systems learn and reason through human interactions. When you define cognitive computing, you get a group of technologies recognized to do a certain specialized activity that aids human intellect. In general, these are smart decision support systems that employ better data and better algorithms to interpret information more effectively.
Few Features of Cognitive AI?
Here are a few cognitive AI elements that aid in the implementation of cognitive computing in enterprises and applications.
Interactive Features
- Because human-computer interaction is a fundamental component of cognitive systems, they must interact bifacially.
- It should understand human input and offer appropriate results by utilizing natural language processing and deep learning.
- This capability has already been incorporated into certain intelligent chatbots.
Adaptive features
- Cognitive computing systems should be adaptable to deal with data changes and goal development.
- The solutions developed should represent the human brain’s ability to learn and adapt to its surroundings.
- Computers cannot be given individual tasks. As a result, they evolve based on data gathering and comprehension of the objectives and needs.
Contextual features
- This is an essential aspect of the cognitive process. As a result, cognitive systems must understand it and uncover contextual data such as time, domain, location, tasks, and objectives.
- Furthermore, the systems may pull information from various sources, including organized and unstructured digital and emotional data.
Many people ask this question: how cognitive computing differs from artificial intelligence? Here we have discussed in detail how artificial intelligence differs from cognitive computing.

Cognitive Computing VS Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a term that encompasses all technologies that allow robots to think and act like humans. It encompasses machine learning (ML) & deep learning and image recognition, neural networks, and natural language processing (NLP). Because cognitive computing employs these similar technologies, it is sometimes mistaken for AI. However, the output of these systems, and their interaction with humans, are considerably different.
So, what is artificial intelligence, and how does it vary from cognitive computing? We will examine how both technologies function, with an emphasis on the former and its applications.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
AI is made up of algorithms that determine the optimal method to perform a function or make a decision given a set of restrictions and then take the right action based on their results. AI, like human intelligence, learns from its surroundings and analyzes what it discovers to choose the best course of action or solution to a problem or the best way to execute a task, such as visual identification or speech recognition. AI systems do tasks that normally require human intellect, such as acting as a chatbot or virtual assistant.
What Exactly Is Cognitive Computing?
Cognitive computing systems are fundamentally intelligent decision-making systems. They are intended to equip decision-makers with the data required to make better data-driven decisions. Cognitive computing systems can process massive volumes of data (which humans cannot) and do extensive iterative analytics while modifying their results as fresh data enters the system.
To solve complicated issues, cognitive computing systems use self-learning algorithms that rely on AI technologies such as data mining, image recognition, speech recognition, and natural language processing (NLP). These systems learn, reason, and interact with humans in the same way that humans do. They, like humans, can work with symbols and concepts.
How Cognitive Computing Differs from Artificial Intelligence? The key Differences!
Human Interaction
Cognitive computing systems are designed to think, reason, and recall to provide humans with useful guidance while making decisions. Its insights are meant to be consumed by humans. AI seeks to utilize the best algorithm to provide the most accurate outcome or action. It functions without any human intervention.
Contextual Solutions
Cognitive computing can take into account contradictory and changing information that is contextually relevant to the scenario at hand. Its findings are the product of employing predictive and prescriptive analytics rather than pre-trained algorithms. For example, if an adult in her fifties wanted to know what program to use to build physical strength, AI would recommend the finest program available (maybe suited to an athlete). Cognitive computing, on the other hand, would take her age and aptitude into account and recommend changes to the software. Finally, AI solves issues using algorithms to arrive at a final judgment; cognitive computing offers the relevant knowledge that allows people to make the final decision for themselves. If you are still wondering how AI technology differs from cognitive computing, here we have mentioned a few more differences.

Understanding the Distinction between Artificial Intelligence and Cognitive Computing!
- AI is a larger concept, whereas cognitive computing is a subset of AI technology.
- To make data-driven judgments, AI and cognitive computing take diverse techniques.
- AI technology is primarily focused on problem-solving activities, whereas cognitive computing serves as a complement to help people make better judgments (for example, AI and cognitive computing must deal with large data sets).
- Then, after evaluating all of the data, AI will recommend the best solution to the problem, while cognitive computing will extract useful information to aid decision-making.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, artificial intelligence (AI) employs algorithms to enable robots to think intelligently and make business decisions. Cognitive computing, on the other hand, employs data mining and NLP to replicate human brain processes and reasoning and provide relevant recommendations that humans may use to solve complicated issues. This blog has covered everything you need to differentiate between cognitive computing and artificial intelligence. We have discussed what artificial intelligence is and how it is different from cognitive computing. In short, both of these smart systems help interpret information more effectively.








































































![Essential-Cybersecurity-Tips-for-Small-Businesses-[Protect-Your-Data]-TrendsBeat](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Essential-Cybersecurity-Tips-for-Small-Businesses-Protect-Your-Data-feature-image-template-1024x455.jpg)
















![Top Fitness Trends & Workout Routines to Follow [Stay Fit, Stay Healthy]](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/feature-image-Top-Fitness-Trends-Workout-Routines-to-Follow-Stay-Fit-Stay-Healthy-1024x455.jpg)









![[Weight Loss Medication Health Effects] Side Effects and Best Advice](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/feature-image-Weight-Loss-Medication-Health-Effects-Side-Effects-and-Best-Advice-1024x455.jpg)