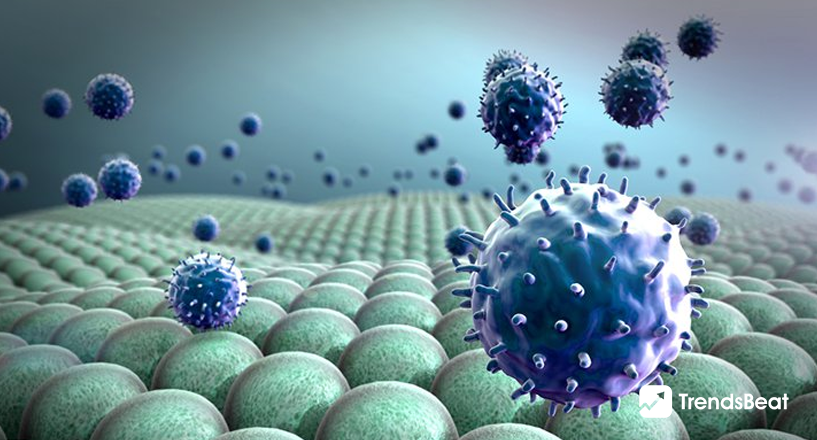
What Are The Latest Breakthroughs In Cancer Treatment And Research?

AI, DNA sequencing, precision oncology, and other technologies are being used by cancer researchers to enhance illness therapy and diagnosis. Cancer treatment breakthroughs include the sequencing of over 12,000 cancer tumors’ DNA and the development of a novel test for identifying pancreatic cancer, one of the deadliest cancers. Gene therapy, targeted therapy, precision medicine, stem cell treatment, nanotechnology-based drugs, and combination therapy are the latest cancer treatment breakthroughs. Read on to learn more about the latest cancer treatments and their benefits.
What Is Immunotherapy And How Has It Impacted Cancer Treatment?
As part of its normal function, the immune system finds and kills abnormal cells, and it most likely prevents or slows the growth of many cancers. Immune cells, for example, can be seen in and around tumors. These cells, known as tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), indicate that the immune system is reacting to the tumor. Individuals whose malignancies have TILs frequently fare better than those whose cancers do not.
Cancer cells can withstand immune system destruction, even though the immune system can prevent or restrict cancer growth. Cancer cells, for example, may:
- Having genetic alterations that reduce their visibility to the immune system.
- They have proteins on their surface that inhibit immune cells.
- Alter the normal cells in the tumor’s vicinity so that they interfere with the immune system’s response to the cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy improves the immune system’s ability to fight cancer.
Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that leverages the immune system’s capacity to prevent, control and destroy cancer. Immunology has already led to key treatment advances for various diseases, from the first preventative vaccination for cervical and liver cancer to the first medication ever demonstrated to lengthen the lives of patients with metastatic melanoma. Yet, each cancer type is distinct, and immunology and immunotherapy affect each malignancy in various ways.
How Is Gene Therapy Being Used To Treat Cancer and What Are The Benefits?
Gene therapy is a method of treating or preventing disease that involves changing the genetic instructions within a person’s cells. Genes are in charge of almost every element of cell life: they encode the code for proteins that allow cells to grow, operate, and divide. Important biological activities may be hampered when a gene is absent or hyperactive. The purpose of gene therapy is to address such issues by addressing them at their source.
Gene therapy can entail replacing defective or missing genes with healthy ones, allowing cells to create functional proteins. It may also entail altering gene regulation so that underactive or hyperactive genes function effectively. Lastly, gene therapy may be utilized to express completely alien genes in cells, causing them to change their function or survival.
Many initiatives are ongoing to adapt gene therapy to cancer treatment. Most are in the early exploratory stages, being researched in laboratory or clinical research studies. However, one technique, known as CAR T-cell therapy, has gotten FDA clearance for use as a therapeutic in specific categories of patients and is anticipated to earn further approvals shortly.
Cancer gene therapy research is currently focused on several areas, including genetically engineered viruses that directly kill cancer cells, gene transfer to alter the abnormal functioning of cancer cells, and immunotherapy (including CAR T-cell therapy), which aids the immune system in finding and killing tumor cells.
What Is Targeted Therapy and How Does It Differ From Traditional Chemotherapy?
Targeted therapy is technically a kind of chemotherapy, although it does not work in the same manner. Chemotherapy kills normal, healthy cells while eliminating cancer cells, which is what distinguishes these two successful cancer therapies. Targeted treatment, on the other hand, exclusively affects malignant cells; normal cells are unaffected.
The following are the distinctions between chemotherapy and targeted therapy:
- Conventional chemotherapy is cytotoxic to cells, which means it harms both healthy and malignant cells.
- Cancer cells are affected by targeted therapy, but normal, healthy cells are usually unaffected.
- Conventional chemotherapy destroys previously existing cancer cells.
- Targeted treatment can prevent cancer cells from multiplying, hence preventing the production of new cells.
Traditional Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy: What’s the Difference?
About Chemotherapy
- Drugs are used in this type of cancer treatment to eliminate malignant cells.
- The technique targets cells at various phases of their life cycle.
- Because these cells are usually fast-growing, these medications can help to interrupt the life cycle of malignant cells.
- One shortcoming of chemotherapy is that the medicine fails to distinguish between diseased and healthy cells, causing normal cells to be harmed as well.
- Normal cells recover from their effects, whereas malignant cells become modified and fail to recover.
Targeted Therapy
- Targeted therapy targets specific malignant cells while causing no damage to normal cells.
- Many forms of cancer cells have different gene modifications and enzymes or proteins that signal malignant cells to multiply and develop.
- These medications target enzymes or proteins that inhibit communication, causing malignant cells to cease growing or disintegrate.
- It alters the underlying mechanism of the cells, focusing on malignant cells and distinguishing them from healthy ones.
- Since it does not harm healthy cells, its side effects differ from other medicines.
What Is Precision Medicine and How Is It Being Used To Treat Cancer?
Doctors have long understood that the same disease can manifest itself differently in various patients and that there is no one-size-fits-all therapy. Precision cancer medicine improves cancer and other illness diagnoses by analyzing the particular genetic composition of tumors to determine the safest and most effective therapies.
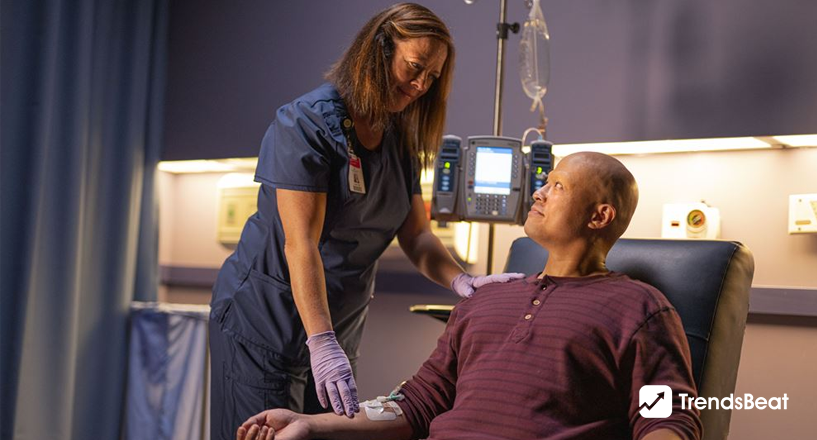

Precision medicine in cancer entails examining DNA from patients’ tumors to detect mutations or other genetic alterations driving their disease. Doctors may therefore be able to choose a therapy for a specific patient’s cancer that best fits, or targets, the responsible mutations in the tumor DNA. Such treatments are becoming increasingly common.
It is critical to recognize that precision medicine is not currently employed for every kind of cancer. The goal is that one day, therapies will be tailored to the exact gene and protein abnormalities found in each individual’s cancer. There is a lot of study being done in this area. Precision medicine is being utilized to aid with treatment options for several of the more prevalent malignancies, including:
- Colorectal cancer
- Lung cancer
- Breast cancer
- Certain types of leukemia
- Certain types of lymphoma
- Melanoma
- Stomach cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Thyroid cancer
- Esophageal cancer
If you have a kind of cancer where treatment choices may be dependent on whether or not the cells contain particular gene or protein modifications, your cancer will almost certainly be tested for them.
Few Final Thoughts
This blog is aimed to provide the information on latest cancer treatment breakthroughs and how different cancer treatments can benefit humans. The blog mentioned above has covered the therapies and treatments that are effective for cancer treatment. Gene therapy, targeted therapy, precision medicine, stem cell treatment, nanotechnology-based drugs, and combination therapy are the latest cancer treatments used to treat cancer.








































































![Essential-Cybersecurity-Tips-for-Small-Businesses-[Protect-Your-Data]-TrendsBeat](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Essential-Cybersecurity-Tips-for-Small-Businesses-Protect-Your-Data-feature-image-template-1024x455.jpg)
















![Top Fitness Trends & Workout Routines to Follow [Stay Fit, Stay Healthy]](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/feature-image-Top-Fitness-Trends-Workout-Routines-to-Follow-Stay-Fit-Stay-Healthy-1024x455.jpg)









![[Weight Loss Medication Health Effects] Side Effects and Best Advice](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/feature-image-Weight-Loss-Medication-Health-Effects-Side-Effects-and-Best-Advice-1024x455.jpg)