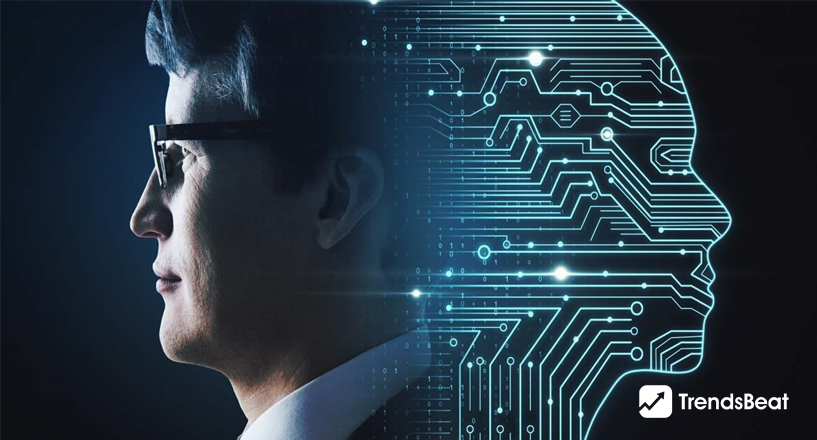
AI vs. Human: Why One-Third of People Can’t Differentiate Humans from AI, and Its Importance

AI is one of today’s hotly debated issues, and there appears to be little agreement on the distinctions and parallels between human intellect and artificial intelligence. Many related discussions, such as trustworthiness, explainability, and ethics, are characterized by implicit anthropocentric and anthropomorphic ideas, such as the pursuit of human-like intellect as the gold standard for artificial intellect. It’s easy to humanize artificial intelligence. We picture befriending Siri or having our self-driving car look out for our best interests. When we think about sophisticated AI, we might envisage robots that “learn” in the same manner that a toddler does. We see them “thinking” or “coming to conclusions” in the same way that we do. Even the phrase “neural networks” evokes visions of a brain-like computer making judgments. According to new research in Minds and Machines by David Watson of the Oxford Internet Institute and the Alan Turing Institute, believing artificial intelligence functions in the same manner as a human brain might be inaccurate and even hazardous. Read this blog to know why one-third of people can’t identify human AI differences.
Why do People find it Difficult to Differentiate between AI and Humans?
There are significant factors that can contribute to the difficulty to distinguish between humans and AI in specific scenarios. Here are the reasons why people struggle with differentiating AI and humans.
AI Advancements: AI technology has advanced significantly in recent years, particularly in natural language processing and machine learning. As a result, chatbots, virtual assistants, and other AI systems that can simulate human-like interactions and behaviors have been developed. As a result, separating AI from humans has gotten increasingly difficult, especially in text-based interactions.

Limited exposure to AI: Not everyone has been exposed to or is familiar with AI technology. Some people may have never experienced advanced AI systems or are unaware of their existence. As a result, individuals may lack the expertise or experience required to distinguish between human and AI interactions.
Context-Specific Limitations: People’s capacity to distinguish between AI and humans may vary depending on the situation or domain. Chatbots, for example, are frequently built to replicate human replies in customer service encounters, making it impossible to tell whether you are engaging with a real person or an AI system. In certain situations, AI systems can even pass the Turing test, which measures a machine’s capacity to demonstrate intelligent behavior that is indistinguishable from human behavior.
Emotional Responses: AI systems are getting better at imitating emotions and empathy. They can create appropriate emotional reactions, making it difficult to distinguish them from genuine human empathy. When the engagement is restricted to text or voice communication, this element becomes more evident.
Only Half Of All Americans Can Tell The Difference Between AI And Human Writing
In news that is sure to break the hearts of authors worldwide, it appears that ChatGPT and other artificial intelligence tools can write just as effectively as humans—at least to a level where the typical American adult cannot tell the difference. The findings are based on a poll done by ToolTester(Opens in a new window), a website dedicated to locating the finest web builders, hosting, and e-commerce solutions. It conducted two polls, the first of which was conducted in late February 2023 among 1,920 American adults, and compared 75 pieces of prose written by AI, by humans, or by AIs and edited by humans. The AI utilized was ChatGPT, which was powered by GPT-3.5, but with the release of GPT-4, ToolTester surveyed an additional 1,394 people in late March with the same questions and themes but with fresh AI-generated text and prompts.

More than half of those polled believed ChatGPT-3.5’s content was authored by a person. Using GPT-4, that figure increased to 63.5%. The results reveal that GPT-4 (used in the paid version of ChatGPT) is at least 16.5% more compelling than the GPT-3.5 copy. Depending on the nature of the writing, AI copy might be more difficult to spot. For example, AI-generated health-related publications are the best at fooling consumers into thinking they were written by humans.
Education & Awareness & Its Impact on Society
Artificial intelligence (AI) systems are rapidly being used in decision-making processes such as recruiting, loan approvals, and legal proceedings. When people can’t tell whether they’re engaging with AI or humans in such vital situations, it might lead to mistrust, perceived prejudices, and even injustices. To reduce these concerns, it is critical to set clear principles and standards for transparency, accountability, and the ethical use of AI technology.
The difficulty in distinguishing people from AI emphasizes the importance of education and awareness programs. Improving public knowledge of AI technology, its potential, and its limits can assist individuals in making well-informed choices during interactions. Promoting digital literacy, critical thinking, and media literacy skills can provide people with the confidence to navigate the emerging AI ecosystem.








































































![Essential-Cybersecurity-Tips-for-Small-Businesses-[Protect-Your-Data]-TrendsBeat](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Essential-Cybersecurity-Tips-for-Small-Businesses-Protect-Your-Data-feature-image-template-1024x455.jpg)
















![Top Fitness Trends & Workout Routines to Follow [Stay Fit, Stay Healthy]](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/feature-image-Top-Fitness-Trends-Workout-Routines-to-Follow-Stay-Fit-Stay-Healthy-1024x455.jpg)









![[Weight Loss Medication Health Effects] Side Effects and Best Advice](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/feature-image-Weight-Loss-Medication-Health-Effects-Side-Effects-and-Best-Advice-1024x455.jpg)



