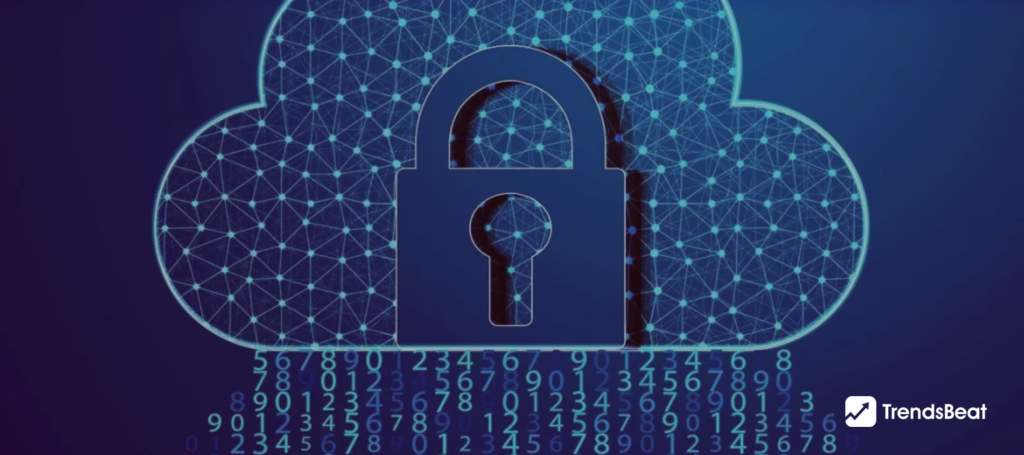
Ransomware Alert: Dish Network Confirms Data Breach by Hackers

DISH, a provider of satellite television programming, recently had a significant system fault that had a negative impact on numerous services. Due to the outage, websites and channels were unavailable, logins were broken, and some people were even unable to pay their bills. There was a nagging feeling that something might have gone wrong in the backend. But later, Dish Network confirmed that it was a dish network ransomware attack and termed it a cybersecurity disaster. The latest public filing with the SEC provided further information about the incident after the disruption was previously referred to as an “internal systems issue” and a “VPN issue”. It was a data breach attempt by hackers.
How Did The Dish Network Ransomware Attack Happen, And What Kind Of Data Was Compromised?
Dish Network was hacked by a hacking gang that launched a dish network ransomware attack on the business, albeit we don’t yet know all the circumstances. Although we don’t know exactly what happened, the hack probably exposed personal information and compromised the company’s data network. In order to access Dish Network’s files, which it later encrypted, the gang discovered network weaknesses that they exploited. The group requested payment from Dish Network in order to decode the files and get the business’s network back up and running. Dish Network’s services are gradually being restored after the attack, and consumers should be able to use them once more. Nevertheless, it is unknown whether Dish Network paid the gang any money.

Dish Network is currently conducting an investigation to look into every area of its network; however, unless sensitive information was stolen, no information must be made public. The file network of the business houses the data of the millions of clients that Dish Network serves. There is no information on the data that the attackers viewed and took, though. At the time being, all we know is that the network was compromised, the company’s file network was severely damaged by the attackers, and the service was interrupted as a result. We’ll have to wait to see if Dish Network ever provides any further details regarding the attack.
HOW TO DEFEND AGAINST A RANSOMWARE ATTACK?
- Don’t give out your personal information to dubious sources who contact you by phone, text, or email. Instead, ignore them. Before initiating a ransomware attack, fraudsters may try to collect personal information from you in order to develop customized phishing messages for you. Contact the sender right away if you have any doubts about the message’s legitimacy.
- Never click on dubious links. Avoid clicking on links found on dubious websites or in spam emails. If you click on malicious links, an automatic download that infects your machine may start.
- Upgrade your operating system and programs. By periodically updating your operating system and software, you may better protect yourself from malware. While executing updates, make sure you utilize the most recent security fixes. This makes it more challenging for scammers to exploit weaknesses in your systems.
- Do not open strange email attachments! Email attachments are another way that ransomware can get into your system. Any suspicious-looking attachments should not be opened. To make sure the email is trustworthy, pay close attention to the sender and confirm that the address is correct. If an attachment asks you to run a macro in order to view it, never open it. By launching a malicious macro when you open an infected attachment, the malware can take over your system. sssssss
- Use only trusted download sources. Never download software or media from unreliable sources to avoid getting infected with ransomware. Choose reliable and trustworthy websites when you want to download. Trust seals can be used to identify certain websites. Check that the “http” in the browser address bar of the page you are visiting has been replaced with “https.” A shield or lock icon might also be visible in the address bar.
- When connecting to public Wi-Fi networks, use VPN services. A realistic ransomware defense approach is to use public Wi-Fi networks with care. If your computer is connected to a public Wi-Fi network, attacks are more likely to occur. Wherever possible, stay away from using public WiFi for sensitive transactions or use a secure VPN service.
How Can Ransomware Be Removed?
There are techniques that might work in some situations, but there is no assurance that victims will be able to stop a ransomware assault and get their data back. In safe mode, for instance, sufferers can restart their computer, install an antimalware program, scan it, and then restore it to a prior, uninfected state.

Moreover, victims could use backup files located on a different disc to recover their systems. Victims could reformat their drive and restore from an earlier backup if the files are in the cloud. System Restore is a feature of Windows devices and their system files that allows users to restore Windows devices and their system files to a specific marked point in time — in this case, before the computer was infected.
Follow these suggestions for a broad, step-by-step procedure to locate and delete the ransomware:
- Make a system backup and make a copy of all crucial or essential files. An organization will be able to restore from a backup if it is unable to retrieve its files.
- Verify that system cleanup or optimization software does not get rid of the infection or other important ransomware files. It is necessary to separate and identify the files first.
- Use anti-malware software to quarantine the virus. Also, confirm that the attackers did not create a backdoor that would have given them access to the same system in the future.
- Define the type of ransomware and the precise encryption technique that was applied. The type of ransomware can be identified with the aid of a decryptor and ransomware recovery tools.
- Files can be decrypted using ransomware recovery tools when they have been located. There is no 100% certainty that the tool will be able to help due to the various and constantly changing ransomware techniques.








































































![Essential-Cybersecurity-Tips-for-Small-Businesses-[Protect-Your-Data]-TrendsBeat](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Essential-Cybersecurity-Tips-for-Small-Businesses-Protect-Your-Data-feature-image-template-1024x455.jpg)
















![Top Fitness Trends & Workout Routines to Follow [Stay Fit, Stay Healthy]](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/feature-image-Top-Fitness-Trends-Workout-Routines-to-Follow-Stay-Fit-Stay-Healthy-1024x455.jpg)









![[Weight Loss Medication Health Effects] Side Effects and Best Advice](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/feature-image-Weight-Loss-Medication-Health-Effects-Side-Effects-and-Best-Advice-1024x455.jpg)



