What Are The 5 Vs of Big Data? What 4 V’s Are Related to The Big Data Concept?
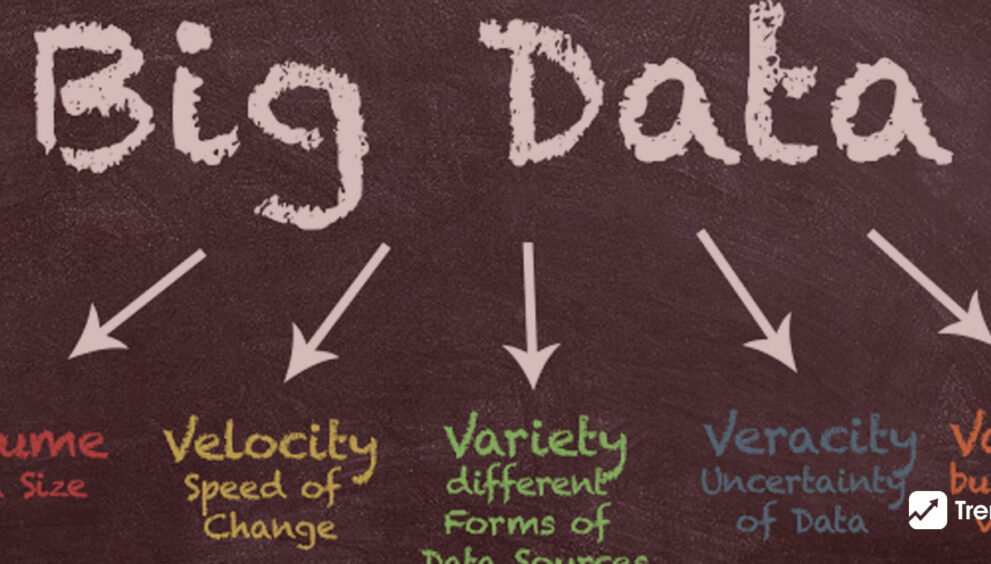
The five primary and intrinsic features of big data are the 5 V’s (velocity, volume, value, variety, and veracity). Knowing the 5 VS of big data enables data scientists to extract more value from their data while also enabling the scientists’ company to become more customer-centric. Big data was only discussed in the early part of this century in terms of the three V’s: volume, velocity, and variety. Two more V’s (value and veracity) have been developed throughout time to assist data scientists in better expressing and explaining the qualities of big data. Read on to learn what is big data analytics and the 5 VS of big data.
What Is Big Data?
Big data is a collection of unstructured, semi-structured, and structured data gathered by businesses. This information may be mined for insights and applied to machine learning projects, predictive modelling, and other advanced analytics applications.
Big data may be utilized to boost value by improving operations, providing better customer service, and creating targeted marketing campaigns. Big data, for example, may give businesses important insights into their customers, which can then be utilized to optimize marketing strategies to increase customer engagement and conversion rates.
It is crucial to the survival of successful businesses. Decision makers must be aware of its difficulties, often known as its five V’s, to maximize its value. These are the sheer volume, the exponential velocity, the variety, the necessity to validate it, and the problem of extracting value from its content.
The 5 Vs of Big Data! Big Data Characteristics!
Big data is a collection of data from various sources that is frequently defined by five characteristics: volume, value, variety, velocity, and veracity. Here we have mentioned the 5 big data characteristics. Read on to know what the 5 vs of big data are.
Volume refers to the magnitude and quantity of large data that businesses manage and analyze.
Value: the most essential “V” from a business standpoint, the value of big data typically stems from insight discovery and pattern identification, which leads to more productive operations, greater customer connections, and other clear and verifiable commercial benefits.
Variety: the breadth and diversity of different data types, such as unstructured data, semi-structured data, and raw data.
Velocity: the rate at which businesses receive, store, and manage data – for example, the number of social media posts or search queries received in a given day, an hour, or another unit of time.
Veracity: The “truth” or accuracy of data and information assets, which often determines executive-level confidence, which is referred to as veracity.
The In-depth Understanding of the 5 VS of Big Data!
Volume
Volume is the first of the five V’s of big data, and it relates to the quantity of data that exists. Volume is the foundation of big data since it is the initial amount and amount of data collected. The volume of data determines whether it is called Big Data or not. The fast-expanding volume of data is attributed to cloud computing traffic, IoT traffic, mobile traffic, and other factors. When the volume of data is big enough, it is referred to as big data. However, it will fluctuate based on the available processing power on the market.

Velocity
Companies need data to flow swiftly – as near to real-time as feasible. Velocity might be more essential than volume since it can offer us a stronger competitive edge. It is sometimes preferable to have limited data in real-time rather than a large amount of data at a slow speed. Velocity represents the pace of data as well as how information moves continually. For example, a customer using wearable technology with a sensor connected to a network will continue to collect and communicate data to the source. It’s not a one-time occurrence. Imagine millions of devices executing this operation concurrently and indefinitely, and you can understand why volume and velocity are the two most important features.
Variety- One of the Crucial 5 Vs of Big Data
The fifth of the five V’s of big data is variety. The term “variety” refers to the many forms of data. An organization may collect data from various data sources, the value of which may vary. Data may originate from both inside and outside of a company. The standardization and sharing of all data collected are difficult in variety.
Data collected might be unstructured, semi-structured, or structured. Unstructured data is disorganized data that arrives in many files or types. Unstructured data is typically not a suitable fit for a standard relational database since it does not fit into traditional data models. Semi-structured data is information that has not been arranged into a specific repository but does have related information, such as metadata. As a result, it is easier to process than unstructured data. Structured data, on the other hand, is information that has been arranged into a prepared repository. This means that the data is more easily accessible for efficient data processing and analysis.
Veracity
It relates to the assurance of data quality/integrity/credibility/accuracy. Because the data is derived from many sources, we must validate it before applying it to business insights.
Value- Another Significant 5 Vs of Big Data
Value is the fifth and final V of big data. This refers to the value that big data may give, and it is closely related to what businesses can do with the data they collect. The ability to extract value from big data is required since the value of big data rises considerably based on the insights that can be gleaned from it. Organizations can obtain and analyze data using the same big data techniques, but how they extract value from that data should be unique to them.

The Four V’s Associated with the Big Data Concept!
Our world is now datafied. Every day, 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are created, ranging from data that shows activity, such as our Google searches and online shopping habits, to communication and conversations via text, smartphones, and virtual assistants, and all the pictures and videos we take, to sensor data collected by internet-of-things devices and more. The better firms and organizations manage and safeguard their data, the more likely they are to be successful. How can you tell whether your data contains the attributes that define it as big? Most people consider data to be big if it possesses the four Vs: volume, velocity, variety, and veracity. These 4 Vs. are majorly associated with big data, but we can’t overlook the significance of the fifth v, value. For data to be helpful to an organization, it must produce value—a vital fifth feature of big data that must not be overlooked.
Conclusion
The five VS. of big data are volume, value, variety, velocity, and veracity. Big data is a collection of unstructured, semi-structured, and organized business data. This data may be analyzed for insights and used in machine learning projects, predictive modelling, and other advanced analytics applications. Throughout this blog, we have discussed the five VS. of big data analytics and the 4 VS of big data concept.








































































![Essential-Cybersecurity-Tips-for-Small-Businesses-[Protect-Your-Data]-TrendsBeat](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Essential-Cybersecurity-Tips-for-Small-Businesses-Protect-Your-Data-feature-image-template-1024x455.jpg)
















![Top Fitness Trends & Workout Routines to Follow [Stay Fit, Stay Healthy]](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/feature-image-Top-Fitness-Trends-Workout-Routines-to-Follow-Stay-Fit-Stay-Healthy-1024x455.jpg)









![[Weight Loss Medication Health Effects] Side Effects and Best Advice](https://trendsbeat.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/feature-image-Weight-Loss-Medication-Health-Effects-Side-Effects-and-Best-Advice-1024x455.jpg)



